BOB Gateway: Bitcoin Intents
Introduction
Bitcoin users can easily onboard to the BOB Hybrid L2 without previously holding any Ethereum assets. This page explains the structure of BOB Gateway, an intent-based bridge that coordinates peer-to-peer swaps between users and liquidity providers (LPs). Cross-chain transfers are secured by verifying Bitcoin transaction proofs with an on-chain light client, avoiding the need for an oracle. Optional intents, such as staking, lending, and swapping a small amount of ETH for transaction fees can all be accomplished while only requiring a single Bitcoin transaction from the user.
How Gateway Works
- Liquidity providers (LPs) temporarily lock wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC or tBTC) in escrow smart contracts on BOB.
- A user makes a request to the (trusted) relayer to reserve some of the available liquidity.
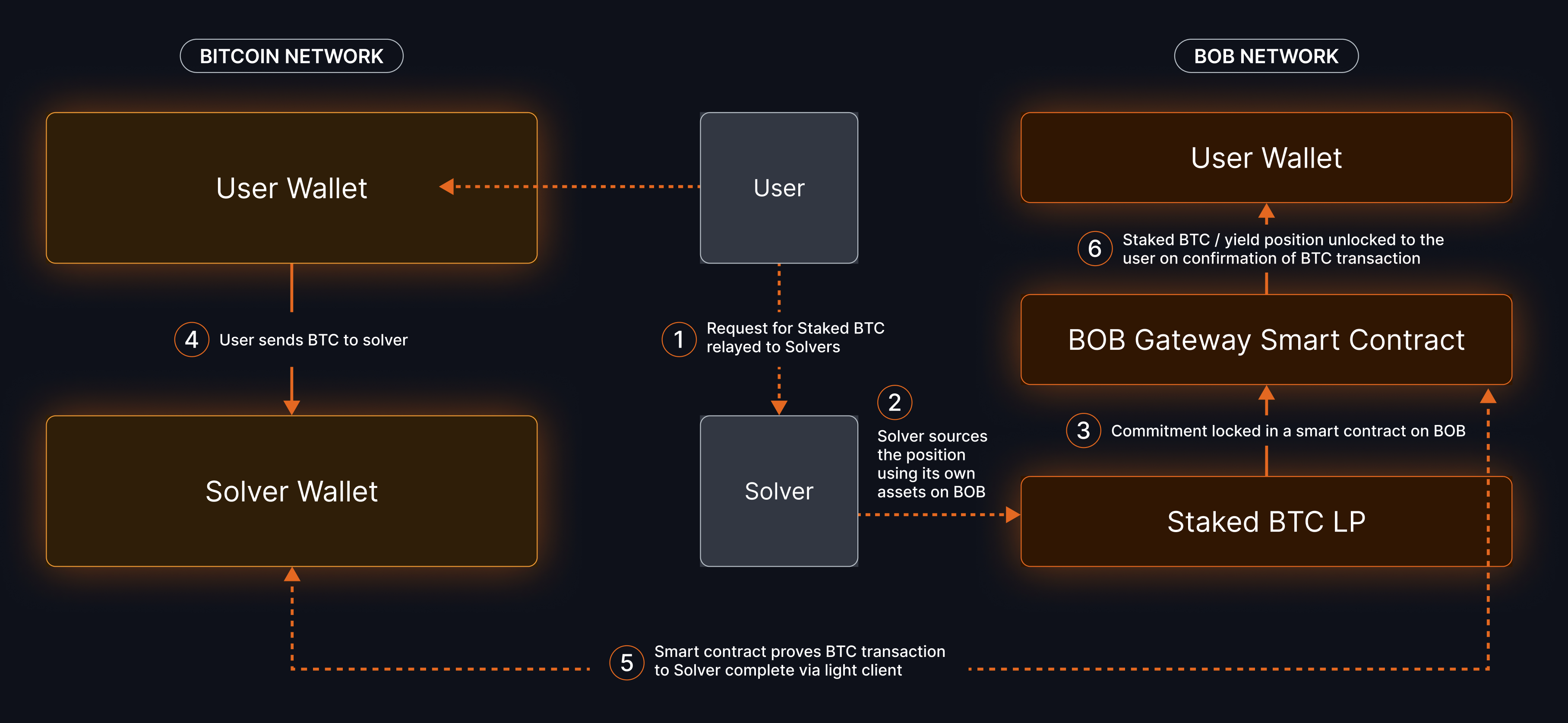
- The user sends BTC to the liquidity provider's Bitcoin address. A hash of the user's order is included in the
OP_RETURNof their transaction, including data such as the recipient's EVM address on BOB. - The relayer trustlessly verifies the user's Bitcoin transaction by submitting a merkle proof to an on-chain Light Client, granting the relayer permission to withdraw the LP's wrapped Bitcoin without needing to use an oracle.
- Gateway sends the LP's wrapped Bitcoin to the user's EVM address. If the user requested a Bitcoin LST/LRT, that token is minted using the LP's wrapped Bitcoin before it is sent to the user.
Architecture
User Flow
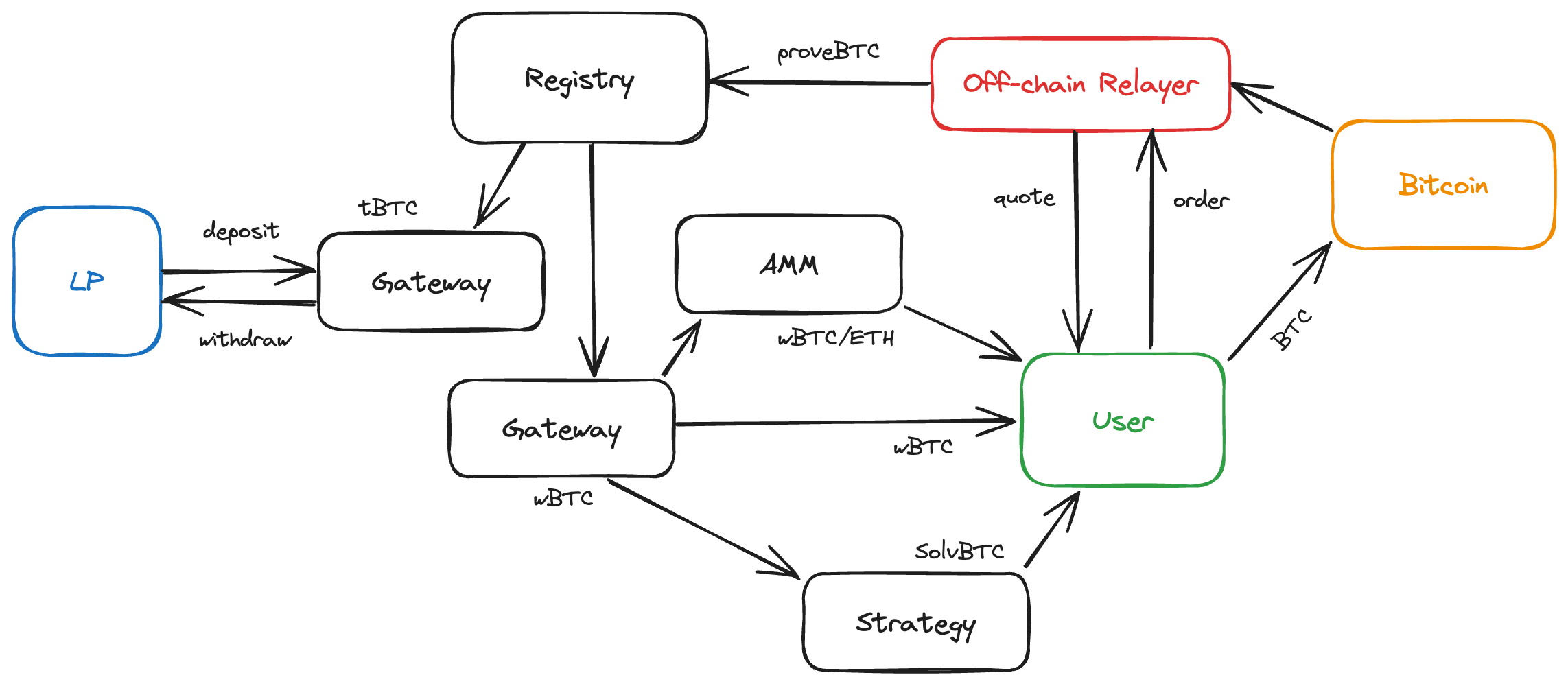
- User requests to swap BTC for e.g. tBTC/WBTC or stake BTC for e.g., SolvBTC.BBN
- User gets "quote" which gateway contract to use
- User creates "order" with relayer based on available liquidity
- User creates tx and updates order with txid - should be done before publishing tx to avoid conflicts
- Relayer monitors Bitcoin chain and executes swap when txid seen
Any frontend can integrate with Gateway by following the BOB docs.
Liquidity Provider (LP) Flow
- LP asks relayer to deploy a gateway contract (permissioned at the moment because BOB pays for fees).
- LP deposits wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC, tBTC, FBTC) in the contract.
- LP can only withdraw or update fees after a delay so that the relayer has time to finish open orders.
- Relayer will not accept new orders during this delay until reset.
Example Complex Order Flows
Swapping BTC for WBTC and gas
- BOB creates a Gateway contract from the Registry
- LP deposits WBTC into the Gateway contract
- User request a quote from the off-chain relayer to swap BTC for WBTC and to add ETH for gas fees
- Off-chain relayer provides the quote
- Users places an order with the relayer
- User sends BTC to the LPs Bitcoin address
- Off-chain relayer monitors the Bitcoin chain for the transaction (user to LP)
- Off-chain relayer sends the merkle proof to the Gateway contract which:
- Unlocks the WBTC from the Gateway contract
- Swaps a small portion of the WBTC to ETH and sends it to the user
- Sends the remaining WBTC to the user
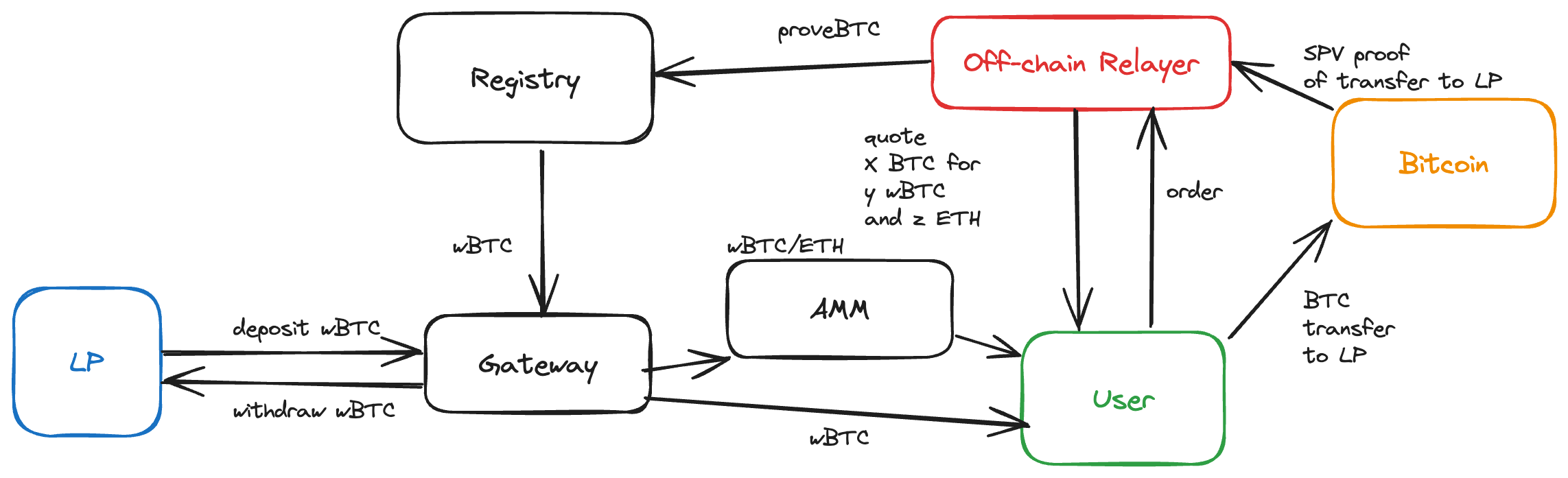
Staking BTC for SolvBTC.BBN and swap for gas
All steps are the same as the swap flow, except for step 8 when the BTC proof is submitted:
- Unlocks the WBTC from the Gateway contract
- Swaps a small portion of the WBTC to ETH and sends it to the user
- Sends the remaining WBTC to the Solv contracts to stake WBTC for SolvBTC. Stakes the solvBTC for solvBTC.BBN. Sends the SolvBTC.BBN to the user.